16 results filtered with: David Goulding, Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute

- Digital Images
- Online
Trichuris muris is a parasitic nematode affecting mice. Following ingestion, T. muris eggs hatch in the large intestine where they develop into adults. The anterior end of the worm burrows into the lining of the gut, leaving the posterior end protruding into the lumen of the gut. The worms mate in this orientation, and the resulting eggs are released in to the gut lumen and shed faecally.
David Goulding, Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute
- Digital Images
- Online
Salmonella Typhimurium
David Goulding, Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute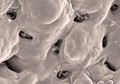
- Digital Images
- Online
Clostridium difficile infected mouse caecum
David Goulding, Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute
- Digital Images
- Online
Shigella flexneri invading embryonic stem cell
David Goulding, Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute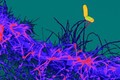
- Digital Images
- Online
Salmonella detection by human epithelial type-2 cell
David Goulding, Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute
- Digital Images
- Online
Schistosoma mansoni flatworm, male with female
David Goulding, Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute
- Digital Images
- Online
Clostridium difficile infected mouse caecum
David Goulding, Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute
- Digital Images
- Online
Group A Streptococci are a species of gram-positive bacteria responsible for causing a number of pyogenic (pus-producing) infections including impetigo, scarlet fever and pneumonia. Further fatal complications arising from infection include the development of meningitis and sepsis.
David Goulding, Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute
- Digital Images
- Online
Group A Streptococci are a species of gram-positive bacteria responsible for causing a number of pyogenic (pus-producing) infections including impetigo, scarlet fever and pneumonia. Further fatal complications arising from infection include the development of meningitis and sepsis.
David Goulding, Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute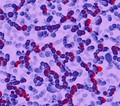
- Digital Images
- Online
Group A Streptococci are a species of gram-positive bacteria responsible for causing a number of pyogenic (pus-producing) infections including impetigo, scarlet fever and pneumonia. Further fatal complications arising from infection include the development of meningitis and sepsis.
David Goulding, Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute
- Digital Images
- Online
Human macrophage rupturing after infection with Chlamydia
David Goulding, Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute
- Digital Images
- Online
Group A Streptococci are a species of gram-positive bacteria responsible for causing a number of pyogenic (pus-producing) infections including impetigo, scarlet fever and pneumonia. Further fatal complications arising from infection include the development of meningitis and sepsis.
David Goulding, Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute
- Digital Images
- Online
Clostridium difficile colony
David Goulding, Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute
- Digital Images
- Online
Salmonella Typhimurium infection of a human epithelial cell
David Goulding, Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute
- Digital Images
- Online
Bodo saltans ingesting bacteria
David Goulding, Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute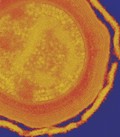
- Digital Images
- Online
Clostridium difficile
David Goulding, Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute