33 results filtered with: Immune response
- Digital Images
- Online
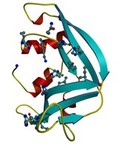
Eosinophil-derived neurotoxin
K R Acharya
- Digital Images
- Online
Trichuris muris is a parasitic nematode affecting mice. Following ingestion, T. muris eggs hatch in the large intestine where they develop into adults. The anterior end of the worm burrows into the lining of the gut, leaving the posterior end protruding into the lumen of the gut. The worms mate in this orientation, and the resulting eggs are released in to the gut lumen and shed faecally.
David Goulding, Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute- Books
Invertebrate immunity : mechanisms of invertebrate vector-parasite relations / edited by Karl Maramorosch, Robert E. Shope.
Date: 1975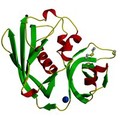
- Digital Images
- Online
Streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin A1
K R Acharya
- Digital Images
- Online
Staphylococcal enterotoxin C2
K R Acharya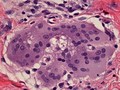
- Digital Images
- Online
Multinucleated giant cell containing an asteroid, microscopy.
William R. Geddie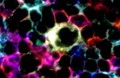
- Digital Images
- Online
Cells interacting to cause immune response
Peter Lane and Fiona McConnell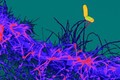
- Digital Images
- Online
Salmonella detection by human epithelial type-2 cell
David Goulding, Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute
- Digital Images
- Online
Schistosoma mansoni flatworm, male with female
David Goulding, Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute- Books
Cellular functions in immunity and inflammation / editors-in-chief Joost J. Oppenheim, David L. Rosenstreich, Michael Potter.
Date: [1981], ©1981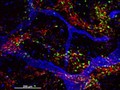
- Digital Images
- Online
Cellular architecture of normal human skin imaged by whole mount tissue microscopy. Human skin has a rich network of white blood cells (specifically dendritic cells, T cells and macrophages) which form sheaths around blood vessels (string-like structures). A network of lymphatic vessels (ribbon-like structures) is also present. In this image, human skin lymphatic vessels (stained for LYVE-1; blue) and white blood cells comprised of dendritic cells (stained for CD11c; green) and T cells (stained for CD3; red) can be seen. Some macrophages also express the protein LYVE-1 similar to lymphatic vessel cells which can be appreciated as blue cells within and in between the sheaths of white blood cells. This normal cellular architecture is grossly disrupted in diseased skin (see related images). X10 magnification. Scale bar (white) represents 200 micrometres.
Dr. Xiao-nong Wang, Human Dendritic Cell Laboratory, Newcastle University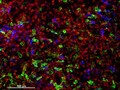
- Digital Images
- Online
Cellular architecture of human skin lymphoma imaged by whole mount tissue microscopy. Normal human skin has a rich network of white blood cells (specifically dendritic cells, T cells and macrophages) which form sheaths around blood vessels. In diseased skin, such as in skin lymphoma as seen here, this normal architecture becomes distorted. In this image, lots of T cells (stained for CD3; red), dendritic cells (stained for CD11c; green) and macrophages (stained for LYVE-1; blue) have infiltrated the skin. X20 magnification. Scale bar (white) represents 100 micrometres.
Dr. Xiao-nong Wang, Human Dendritic Cell Laboratory, Newcastle University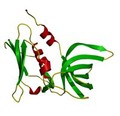
- Digital Images
- Online
Toxic shock syndrome toxin
K R Acharya- Books
Generation and effector functions of regulatory lymphocytes / [edited by Gregory Bock and Jamie Goode].
Symposium on Generation and Effector Functions of Regulatory Lymphocytes (2002 : Novartis Foundation)Date: 2003
- Digital Images
- Online
Cellular architecture of normal human skin imaged by whole mount tissue microscopy. Human skin has a rich network of white blood cells (specifically dendritic cells, T cells and macrophages) which form sheaths around blood vessels. This image was taken less than 20 micrometres beneath the junction that joins the dermal and epidermal layers of the skin (dermo-epidermal junction). At this level, dendritic cells (stained for CD11c; green) form clusters around and between blood capillary loops (stained for CD31; red). The blind-ended tips of initial lymphatic vessels are just visible (stained for LYVE-1; blue) at this level. This normal cellular architecture is grossly disrupted in diseased skin (see related images). Scale bar (white) represents 200 micrometres.
Dr. Xiao-nong Wang, Human Dendritic Cell Laboratory, Newcastle University
- Digital Images
- Online
Cellular architecture of normal human skin imaged by whole mount tissue microscopy. Human skin has a rich network of white blood cells (specifically dendritic cells, T cells and macrophages) which form sheaths around blood vessels. In this image, T cells (stained for CD3; red) dendritic cells (stained for MHC class II; green) and macrophages (stained for LYVE-1; blue with some cells showing a tinge of green) can be seen. Cell nuclei have been stained with DAPI (grey). This normal cellular architecture is grossly disrupted in diseased skin (see related images). X10 magnification. Scale bar (white) represents 200 micrometres.
Dr. Xiao-nong Wang, Human Dendritic Cell Laboratory, Newcastle University
- Books
- Online
Cell therapeutics / by William Addison.
Addison, William, 1802-1881.Date: 1856- Books
Host-defense mechanisms against infection / Anthony S. Fauci.
Fauci, Anthony S., 1940-Date: [1982]
- Digital Images
- Online
Cellular architecture of normal human skin imaged by whole mount tissue microscopy. Human skin has a rich network of white blood cells (specifically dendritic cells, T cells and macrophages) which form sheaths around blood vessels. In this image, T cells (stained for CD3; red) dendritic cells (stained for MHC class II; green) and macrophages (stained for LYVE-1; blue with some cells showing a tinge of green) can be seen. Cell nuclei have been stained with DAPI (grey). This normal cellular architecture is grossly disrupted in diseased skin (see related images). X20 magnification. Scale bar (white) represents 100 micrometres.
Dr. Xiao-nong Wang, Human Dendritic Cell Laboratory, Newcastle University- Books
The secretory immunologic system : proceedings of a conference on the secretory immunologic system December 10-13, 1969, Vero Beach, Florida / [edited by Delbert H. Dayton, Jr. [and others].
Conference on the Secretory Immunologic System (1969 : Vero Beach, Fla.)Date: [1971]- Books
Developments in lymphoid cell biology / A. Arthur Gottlieb.
Gottlieb, A. Arthur (Abraham Arthur), 1937-1998.Date: [1974]
- Digital Images
- Online
Staphylococcal enterotoxin A
K R Acharya
- Digital Images
- Online
Cellular architecture of normal human skin imaged by whole mount tissue microscopy. Human skin has a rich network of white blood cells (specifically dendritic cells, T cells and macrophages) which form sheaths around blood vessels. This image was taken directly beneath the junction that joins the dermal and epidermal layers of the skin (dermo-epidermal junction). At this level, the capillary network (stained for CD31; red) is visualised against a lawn of autofluorescent dermal papillae (finger-like projections of the dermis; green) scattered with dendritic cells (stained for CD11c; green) and macrophages (stained for LYVE-1; blue). This normal cellular architecture is grossly disrupted in diseased skin (see related images). Scale bar (white) represents 200 micrometres.
Dr. Xiao-nong Wang, Human Dendritic Cell Laboratory, Newcastle University
- Digital Images
- Online
Human macrophage rupturing after infection with Chlamydia
David Goulding, Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute
- Digital Images
- Online
Cellular architecture of normal human skin imaged by whole mount tissue microscopy. Human skin has a rich network of white blood cells (specifically dendritic cells, T cells and macrophages) which form sheaths around blood vessels. In this image, blood vessels (string-like structures stained for CD31; green), lymphatic vessels (ribbon-like structures stained for LYVE-1; blue) and T cells (stained for CD3; red) can be seen. T cells are only found around dermal blood vessels. Macrophages (stained for LYVE-1; blue) are also present. This normal cellular architecture is grossly disrupted in diseased skin (see related images). X10 magnification. Scale bar (white) represents 200 micrometres.
Dr. Xiao-nong Wang, Human Dendritic Cell Laboratory, Newcastle University