95 results filtered with: Nucleus

- Digital Images
- Online
Meiosis
NIMR, Francis Crick Institute
- Digital Images
- Online
Human chromosomes in metaphase. The chromatin is stained red and the "glue" that holds the two chromatids together is highlighted in yellow. This glue is a proteinaceous complex called cohesin. Once all the chromosomes are attached to the spindle, the cohesin complex breaks down, allowing the two chromatids to separate and move to opposite poles of the cell.
Matthew Daniels
- Digital Images
- Online
Kidney cell showing nucleus and mitochondria
University of Edinburgh
- Digital Images
- Online
Meiosis
NIMR, Francis Crick Institute
- Digital Images
- Online
Cell from a squamous cell carcinoma cell line. It has been frozen and split open to reveal its nucleus.
Anne Weston, Francis Crick Institute
- Digital Images
- Online
Human chromosomes in metaphase. The chromosomes are all aligned and at this stage they are attached to the spindle (not visible in this image).
Matthew Daniels
- Digital Images
- Online
White blood cell - polymorphonuclear leucocyte - neutrophil
University of Edinburgh
- Digital Images
- Online
Organelles in a pancreas cell
University of Edinburgh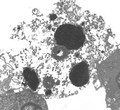
- Digital Images
- Online
TEM gut cell undergoing secondary necrosis
Dr Jeremy Skepper
- Digital Images
- Online
Avian blood
Royal Veterinary College
- Digital Images
- Online
Human chromosomes in early anaphase. At this stage the chromosomes have started to separate from each other and move towards opposite poles of the cell. The chromatin appears grey and the kinetochores are pink.
Matthew Daniels
- Digital Images
- Online
Human cell in interphase showing the tubulin component of the cytoskeleton in green, the DNA in blue and the kinetochores in pink.
Matthew Daniels
- Digital Images
- Online
Avian blood
Royal Veterinary College
- Digital Images
- Online
Human chromosomes in telophase. The chromosomes have separated and decondensed, and the new nuclear envelope forms.
Matthew Daniels
- Digital Images
- Online
Slow muscle fibres in zebrafish myotomes
S. Roy & C. Wolff
- Digital Images
- Online
Macrophage with phagocytic vesicle and lysosomes
University of Edinburgh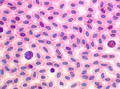
- Digital Images
- Online
Avian blood
Royal Veterinary College
- Digital Images
- Online
Single muscle cell
S. Roy & C. Wolff
- Digital Images
- Online
Mast cell showing histamine granules
University of Edinburgh
- Digital Images
- Online
Meiosis
NIMR, Francis Crick Institute
- Digital Images
- Online
Misreplication of DNA in human fibroblast nucleus
Ezequiel Miron, University of Oxford
- Digital Images
- Online
Meiosis
NIMR, Francis Crick Institute
- Digital Images
- Online
Human cells showing the stages of cell division starting with interphase second from the left on the top. Progressing anticlockwise the stages shown are: early prophase (centrosome not yet separated), late prophase (centrosome separated and DNA condensation), prometaphase (incomplete chromosome attachment), metaphase (chromosomes all attached and aligned), anaphase (chromosome separation), telophase (formation of midbody and cells begin to flatten), early cytokinesis (chromosomes decondensed and nuclear envelope reformed) and late cytokinesis (cells move apart).
Matthew Daniels
- Digital Images
- Online
Drosophila adipose tissue
Christin Bauer
- Digital Images
- Online
Nerve with cell body
University of Edinburgh